Early Modern Letters Online Beta Launch Event
Tags: Bodleian Resources, Databases, Digitization, Mince Pies, Union Catalogue

EMLO screenshots captivate the crowd.

Chris Fletcher sets the scene.

Festive designers and programmers.

The Lister and Lhwyd research teams.

Stephen Clucas and Philip Beeley.

Will Poole and Richard Sharpe.
After a very busy year in private alpha, the Project celebrated the imminent public beta launch of our free union catalogue – Early Modern Letters Online − with a festive reception last Friday. Over eighty students, scholars, librarians, and digital humanists joined us in the historic environment of the Bodleian Library‘s Divinity School, where – over mulled wine, seasonal canapés, and mince pies – they were treated to contextual remarks from Dr Chris Fletcher (Keeper of Special Collections) and Professor Howard Hotson (Director of Cofk), and a full demonstration of the capabilities of the catalogue’s search and discovery, and editorial, interfaces by Project Coordinator Dr James Brown. Many thanks to everyone who contributed to the success of the evening, with a special shout-out to the Bodleian’s Wilma Minty for arranging things with her usual flair.
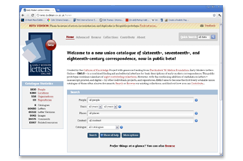
The EMLO homepage.
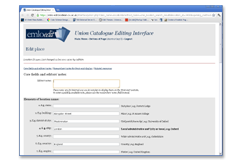
EMLO Edit, the editorial interface.
Early Modern Letters Online – which currently contains 60,480 epistolary records – federates basic metadata from eight contributing sources (including 48,695 sixteenth-, seventeenth-, and eighteenth-century records drawn from the existing card index of correspondence in the Bodleian Library), and allows for their manipulation and further enhancement by means of a sophisticated editorial environment. It will be available to the public from early January 2012.
To stay informed, please watch this space or join the Mailing List. In the meantime, we wish you all a very Happy Holidays!



 The second annual Anglo-French Conference on Scientific Communication and its History will take place in Paris at the
The second annual Anglo-French Conference on Scientific Communication and its History will take place in Paris at the 


 Join
Join 